Pinia和Vuex一樣都是是vue的全局狀態管理器。其實Pinia就是Vuex5,只不過為了尊重原作者的貢獻就沿用了這個看起來很甜的名字Pinia。
本文將通過Vue3的形式對兩者的不同實現方式進行對比,讓你在以后工作中無論使用到Pinia還是Vuex的時候都能夠游刃有余。
既然我們要對比兩者的實現方式,那么我們肯定要先在我們的Vue3項目中引入這兩個狀態管理器(實際項目中千萬不要即用Vuex又用Pinia,不然你會被同事請去喝茶的。下面就讓我們看下它們的使用方式吧
安裝
-
Vuex
-
Pinia
掛載Vuex
在src目錄下新建vuexStore,實際項目中你只需要建一個store目錄即可,由于我們需要兩種狀態管理器,所以需要將其分開并創建兩個store目錄
新建vuexStore/index.js
import{ createStore } from'vuex'
exportdefaultcreateStore({
//全局state,類似于vue種的data
state {
return{
vuexmsg: "hello vuex",
name: "xiaoyue",
};
},
//修改state函數
mutations: {
},
//提交的mutation可以包含任意異步操作
actions: {
},
//類似于vue中的計算屬性
getters: {
},
//將store分割成模塊(module),應用較大時使用
modules: {
}
})
main.js引入
import{ createApp } from'vue'
importApp from'./App.vue'
importstore from'@/vuexStore'
createApp(App).use(store).mount( '#app')
App.vue測試
< template>
< div> </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ useStore } from'vuex'
letvuexStore = useStore
console.log(vuexStore.state.vuexmsg); //hello vuex
</ >
頁面正常打印hello vuex說明我們的Vuex已經掛載成功了
Pinia
-
main.js引入
importApp from"./App.vue";
import{createPinia} from'pinia'
constpinia = createPinia
createApp(App).use(pinia).mount( "#app");
-
創建Store
src下新建piniaStore/storeA.js
import{ defineStore } from"pinia";
exportconststoreA = defineStore( "storeA", {
state: => {
return{
piniaMsg: "hello pinia",
};
},
getters: {},
actions: {},
});
-
App.vue使用
< div> </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
console.log(piniaStoreA.piniaMsg); //hello pinia
</ >
從這里我們可以看出pinia中沒有了mutations和modules,pinia不必以嵌套(通過modules引入)的方式引入模塊,因為它的每個store便是一個模塊,如storeA,storeB... 。
在我們使用Vuex的時候每次修改state的值都需要調用mutations里的修改函數(下面會說到),因為Vuex需要追蹤數據的變化,這使我們寫起來比較繁瑣。而pinia則不再需要mutations,同步異步都可在actions進行操作,至于它沒有了mutations具體是如何最終到state變化的,這里我們不過多深究, 大概好像應該是通過hooks回調的形式解決的把(我也沒研究過,瞎猜的。
修改狀態
獲取state的值從上面我們已經可以一目了然的看到了,下面讓我們看看他倆修改state的方法吧
vuex
vuex在組件中直接修改state,如App.vue
< template>
< div> {{vuexStore.state.vuexmsg}} </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ useStore } from'vuex'
letvuexStore = useStore
vuexStore.state.vuexmsg = 'hello juejin'
console.log(vuexStore.state.vuexmsg)
</ >
可以看出我們是可以直接在組件中修改state的而且還是響應式的,但是如果這樣做了,vuex不能夠記錄每一次state的變化記錄,影響我們的調試。
當vuex開啟嚴格模式的時候,直接修改state會拋出錯誤,所以官方建議我們開啟嚴格模式,所有的state變更都在vuex內部進行,在mutations進行修改。例如vuexStore/index.js:
import{ createStore } from"vuex";
exportdefaultcreateStore({
strict: true,
//全局state,類似于vue種的data
state: {
vuexmsg: "hello vuex",
},
//修改state函數
mutations: {
setVuexMsg(state, data) {
state.vuexmsg = data;
},
},
//提交的mutation可以包含任意異步操作
actions: {},
//類似于vue中的計算屬性
getters: {},
//將store分割成模塊(module),應用較大時使用
modules: {},
});
當我們需要修改vuexmsg的時候需要提交setVuexMsg方法,如App.vue
< template>
< div> {{ vuexStore.state.vuexmsg }} </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ useStore } from'vuex'
letvuexStore = useStore
vuexStore.commit( 'setVuexMsg', 'hello juejin')
console.log(vuexStore.state.vuexmsg) //hello juejin
</ >
或者我們可以在actions中進行提交mutations修改state:
import{ createStore } from"vuex";
exportdefaultcreateStore({
strict: true,
//全局state,類似于vue種的data
state {
return{
vuexmsg: "hello vuex",
}
},
//修改state函數
mutations: {
setVuexMsg(state, data) {
state.vuexmsg = data;
},
},
//提交的mutation可以包含任意異步操作
actions: {
asyncgetState({ commit }) {
//const result = await xxxx 假設這里進行了請求并拿到了返回值
commit( "setVuexMsg", "hello juejin");
},
}
});
組件中使用dispatch進行分發actions
< template>
< div> {{ vuexStore.state.vuexmsg }} </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ useStore } from'vuex'
letvuexStore = useStore
vuexStore.dispatch( 'getState')
</ >
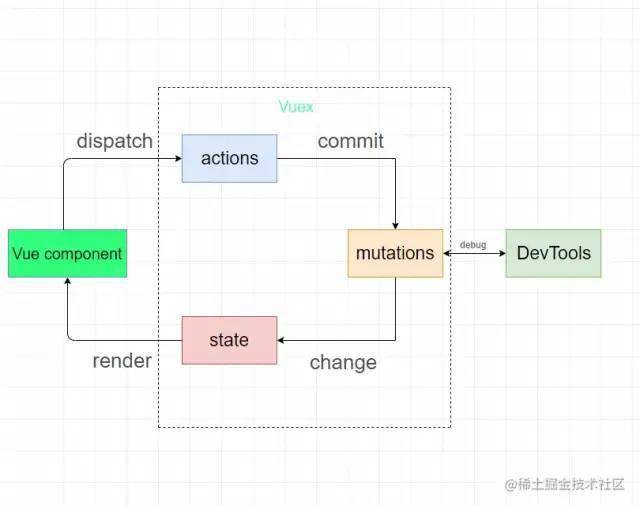
一般來說,vuex中的流程是首先actions一般放異步函數,拿請求后端接口為例,當后端接口返回值的時候,actions中會提交一個mutations中的函數,然后這個函數對vuex中的狀態(state)進行一個修改,組件中再渲染這個狀態,從而實現整個數據流程都在vuex內部進行便于檢測。直接看圖,一目了然
Pinia
-
直接修改
相比于Vuex,Pinia是可以直接修改狀態的,并且調試工具能夠記錄到每一次state的變化,如App.vue
< template>
< div> {{ piniaStoreA.piniaMsg }} </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
console.log(piniaStoreA.piniaMsg); //hello pinia
piniaStoreA.piniaMsg = 'hello juejin'
console.log(piniaStoreA.piniaMsg); //hello juejin
</ >
-
$patch
使用$patch方法可以修改多個state中的值,比如我們在piniaStore/storeA.js中的state增加一個name
import{ defineStore } from"pinia";
exportconststoreA = defineStore( "storeA", {
state: => {
return{
piniaMsg: "hello pinia",
name: "xiaoyue",
};
},
getters: {},
actions: {},
});
然后我們在App.vue中進行修改這兩個state
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
console.log(piniaStoreA.name); //xiaoyue
piniaStoreA.$patch({
piniaMsg: 'hello juejin',
name: 'daming'
})
console.log(piniaStoreA.name); //daming
當然也是支持修改單個狀態的如
piniaStoreA. $patch({
name: 'daming'
})
$patch還可以使用函數的方式進行修改狀態
import { storeA } from '@/piniaStore/storeA'
let piniaStoreA = storeA
cartStore.$patch((state) => {
state.name = 'daming'
state.piniaMsg = 'hello juejin'
})
-
在actions中進行修改
不同于Vuex的是,Pinia去掉了mutations,所以在actions中修改state就行Vuex在mutations修改state一樣。其實這也是我比較推薦的一種修改狀態的方式,就像上面說的,這樣可以實現整個數據流程都在狀態管理器內部,便于管理。
在piniaStore/storeA.js的actions添加一個修改name的函數
import{ defineStore } from"pinia";
exportconststoreA = defineStore( "storeA", {
state: => {
return{
piniaMsg: "hello pinia",
name: "xiao yue",
};
},
actions: {
setName(data) {
this.name = data;
},
},
});
組件App.vue中調用不需要再使用dispatch函數,直接調用store的方法即可
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
piniaStoreA.setName( 'daming')
-
重置state
Pinia可以使用$reset將狀態重置為初始值
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
piniaStoreA.$reset
Pinia解構(storeToRefs)
當我們組件中需要用到state中多個參數時,使用解構的方式取值往往是很方便的,但是傳統的ES6解構會使state失去響應式,比如組件App.vue,我們先解構取得name值,然后再去改變name值,然后看頁面是否變化
< template>
< div> {{ name }} </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
let{ piniaMsg, name } = piniaStoreA
piniaStoreA.$patch({
name: 'daming'
})
</ >
瀏覽器展示如下

我們可以發現瀏覽器并沒有更新頁面為daming
為了解決這個問題,Pinia提供了一個結構方法 storeToRefs,我們將組件App.vue使用 storeToRefs解構
< template>
< div> {{ name }} </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
import{ storeToRefs } from'pinia'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
let{ piniaMsg, name } = storeToRefs(piniaStoreA)
piniaStoreA.$patch({
name: 'daming'
})
</ >
再看下頁面變化

我們發現頁面已經被更新成daming了
getters
其實Vuex中的getters和Pinia中的getters用法是一致的,用于自動監聽對應state的變化,從而動態計算返回值(和vue中的計算屬性差不多),并且getters的值也具有緩存特性
Pinia
我們先將piniaStore/storeA.js改為
import{ defineStore } from"pinia";
exportconststoreA = defineStore( "storeA", {
state: => {
return{
count1: 1,
count2: 2,
};
},
getters: {
sum {
console.log( '我被調用了!')
returnthis.count1 + this.count2;
},
},
});
然后在組件App.vue中獲取sum
< template>
< div> {{ piniaStoreA.sum }} </ div>
</ template>
< setup>
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
console.log(piniaStoreA.sum) //3
</ >
讓我們來看下什么是緩存特性。首先我們在組件多次訪問sum再看下控制臺打印
import{ storeA } from'@/piniaStore/storeA'
letpiniaStoreA = storeA
console.log(piniaStoreA.sum)
console.log(piniaStoreA.sum)
console.log(piniaStoreA.sum)
piniaStoreA.count1 = 2
console.log(piniaStoreA.sum)

從打印結果我們可以看出只有在首次使用用或者當我們改變sum所依賴的值的時候,getters中的sum才會被調用
Vuex
Vuex中的getters使用和Pinia的使用方式類似,就不再進行過多說明,寫法如下vuexStore/index.js
import{ createStore } from"vuex";
exportdefaultcreateStore({
strict: true,
//全局state,類似于vue種的data
state: {
count1: 1,
count2: 2,
},
//類似于vue中的計算屬性
getters: {
sum(state){
returnstate.count1 + state.count2
}
}
});
modules
如果項目比較大,使用單一狀態庫,項目的狀態庫就會集中到一個大對象上,顯得十分臃腫難以維護。所以Vuex就允許我們將其分割成模塊(modules),每個模塊都擁有自己state,mutations,actions...。而Pinia每個狀態庫本身就是一個模塊。
Pinia
Pinia沒有modules,如果想使用多個store,直接定義多個store傳入不同的id即可,如:
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
export const storeA = defineStore("storeA", {...});
export const storeB = defineStore("storeB", {...});
export const storeC = defineStore("storeB", {...}); Vuex
一般來說每個module都會新建一個文件,然后再引入這個總的入口index.js中,這里為了方便就寫在了一起
import{ createStore } from"vuex";
constmoduleA = {
state: => ({
count: 1
}),
mutations: {
setCount(state, data) {
state.count = data;
},
},
actions: {
getuser {
//do something
},
},
getters: { ... }
}
constmoduleB = {
state: => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
exportdefaultcreateStore({
strict: true,
//全局state,類似于vue種的data
state {
return{
vuexmsg: "hello vuex",
name: "xiaoyue",
};
},
modules: {
moduleA,
moduleB
},
});
使用moduleA
import{ useStore } from'vuex'
letvuexStore = useStore
console.log(vuexStore.state.moduleA.count) //1
vuexStore.commit( 'setCount', 2)
console.log(vuexStore.state.moduleA.count) //2
vuexStore.dispatch( 'getuser')
一般我們為了防止提交一些mutation或者actions中的方法重名,modules一般會采用命名空間的方式 namespaced: true如moduleA:
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
state: => ({
count: 1,
}),
mutations: {
setCount(state, data) {
state.count = data;
},
},
actions: {
getuser {
//do something
},
},
}
此時如果我們再調用setCount或者getuser
vuexStore.commit('moduleA/setCount', 2)
vuexStore.dispatch('moduleA/getuser')
作者:東方小月






